Infoblox Integration in Ansible 2.5
Infoblox Integration in Ansible 2.5
The Ansible 2.5 open source project release includes the following Infoblox Network Identity Operating System (NIOS) enablement:
- Five modules
- A lookup plugin (for querying Infoblox NIOS objects)
- A dynamic inventory script
For network professionals, this means that existing networking Ansible Playbooks can utilize existing Infoblox infrastructure for IP Address Management (IPAM), using Infoblox for tracking inventory and more. For more information on Infoblox terminology, documentation and examples, refer to the Infoblox website
Let's elaborate on each of these Ansible 2.5 additions. All of the
following examples (and many more) are provided in the network
automation community project, under the infoblox_ansible
GitHub repository. The
integrations for Ansible require that the control node (where Ansible is
being executed from) have the infoblox-client installed. It can be
found here and installed
with pip issuing the pip install infoblox-client command.
Ansible Infoblox Modules
There are five new modules included with Ansible 2.5. They can be currently found in the development branch of the documentation:
- nios_host_record - configure host records
- nios_network - configure networking objects
- nios_network_view - configure networking views
- nios_dns_view - configure DNS views
- nios_zone - configure DNS zones
Here is an example playbook on configuring a IPv4 network using the nios_network module:
--- - hosts: localhost connection: local tasks: - name: set dhcp options for a network nios_network: network: 192.168.100.0/24 comment: sean put a comment here options: - name: domain-name value: ansible.com state: present provider: "{{nios_provider}}"
Since this playbook did not specify the
network_view parameter it will default to the default view. To run the playbook use the
ansible-playbook command:
SEANs-MacBook-Pro:infoblox_ansible sean$ ansible-playbook configure_network.yml PLAY [localhost] *************************************************************************************** TASK [set dhcp options for a network] *************************************************************** changed: [localhost] PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************** localhost : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
We can login to the web https GUI website and look under Data Management -> IPAM where we will see the new network listed:
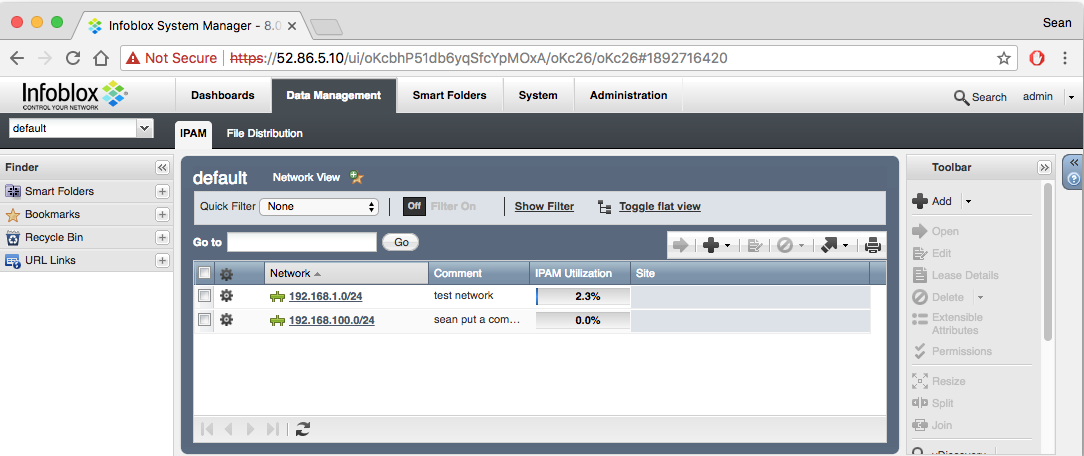
The modules can keep state (where applicable) so when we re-run the playbook instead of saying changed it will just say OK and not perform any changes to Infoblox. This is also referred to as idempotency (referred to in the Ansible Docs glossary).
SEANs-MacBook-Pro:infoblox_ansible sean$ ansible-playbook configure_network.yml PLAY [localhost] *************************************************************************************** TASK [set dhcp options for a network] *************************************************************** ok: [localhost] PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************** localhost : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
Ansible Infoblox Lookup Plugin
Next let's look at the new lookup plugin for Infoblox. The Ansible documentation for the lookup plugin can be found here. The lookup plugin allows us to query different InfoBlox NIOS objects, such as network views, dns views, host records, and more. In my Infoblox IPAM tab (Data Management->IPAM) I have four top of rack leaf switches, and two spine switches defined. I can see them under the list view for managed nodes:
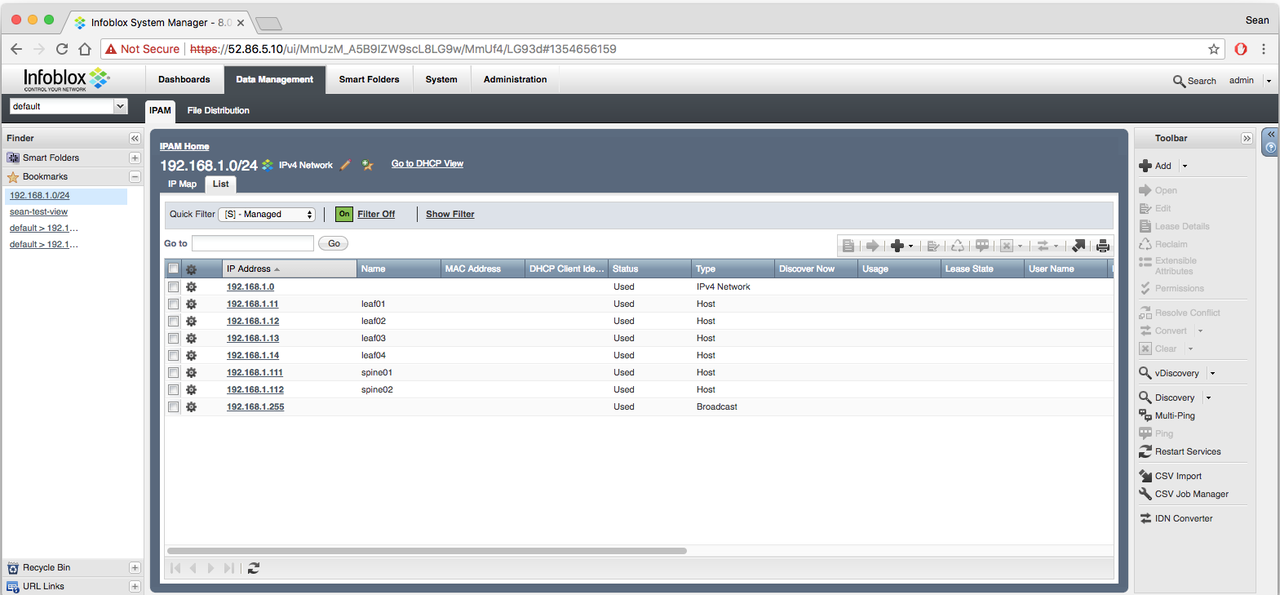
Let's look at an Ansible Playbook snippet focused on grabbing information about a host record:
- name: fetch host leaf01 set_fact: host: "{{ lookup('nios', 'record:host', filter={'name': 'leaf01'}, provider=nios_provider) }}"
We will set the result of the lookup plugin (specified by the keyword nios above) to the variable host. We only want the information for leaf01, so we will filter based on the name. For the full playbook checkout the get_host_record.yml stored on the network automation community.
Run the playbook with the ansible-playbook command:
SEANs-MacBook-Pro:infoblox_ansible sean$ ansible-playbook get_host_record.yml PLAY [localhost] *************************************************************************************** TASK [fetch host leaf01] ****************************************************************************** ok: [localhost] TASK [check the leaf01 return variable] ************************************************************* ok: [localhost] => { <SNIPPET, REST OF OUTPUT REMOVED FOR BREVITY> "host": { "ipv4addrs": [ { "configure_for_dhcp": false, "host": "leaf01", "ipv4addr": "192.168.1.11" } ], } } TASK [debug specific variable (ipv4 address)] ****************************************************** ok: [localhost] => { "host.ipv4addrs[0].ipv4addr": "192.168.1.11" } TASK [fetch host leaf02] ****************************************************************************** ok: [localhost] TASK [check the leaf02 return variable] ************************************************************* ok: [localhost] => { <SNIPPET, REST OF OUTPUT REMOVED FOR BREVITY> "host": { "ipv4addrs": [ { "configure_for_dhcp": false, "host": "leaf02", "ipv4addr": "192.168.1.12" } ], } } PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************** localhost : ok=5 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
The above playbook shows us how we can query Infoblox to grab specific information about Infoblox objects (in this case, specific hosts). These facts can be used through an Ansible play and allow Infoblox to act as a single source of truth for information that may be changing. While the Ansible modules allow you to configure Infoblox, the lookup plugin allows you to grab information from Infoblox to use in subsequent tasks. To read more about Ansible variables, facts and the set_fact module, refer to the Ansible variables documentation.
Ansible Infoblox Dynamic Inventory
Ansible dynamic inventory scripts allow import of inventory from another source like Cobbler, AWS or in this case Infoblox NIOS. You can read more about dynamic inventory on the Ansible dynamic inventory documentation page.
There are two files that need to be located under the
contrib/inventory/ in the Ansible project:
- infoblox.yaml - specifies the provider arguments and optional filters
- infoblox.py - python script that retrieves inventory
Update the infoblox.yaml with your login information to the NIOS
instance. This includes the username, password and an IP address or
hostname. Make sure the infoblox.yaml file is located in /etc/ansible/infoblox.yaml.
To test your setup the python script infoblox.py can be run by executing
python infoblox.py on the command line:
[ec2-user@ip-172-16-103-218 infoblox]$ python infoblox.py { " ": { "hosts": [ "leaf01", "leaf02", "leaf03", "leaf04", "spine01", "spine02" ] }, <SNIPPET, REST OF OUTPUT REMOVED FOR BREVITY>
For this playbook we will create a small debug playbook to print out the inventory_hostname for each host we grab using the infoblox python dynamic inventory script.
--- - hosts: all gather_facts: false tasks: - name: list all hosts debug: var: inventory_hostname delegate_to: localhost
To grab the inventory for a playbook use the
-i parameter and specify
the infoblox.py python script. Run the playbook with the
ansible-playbook command:
[sean@rhel-7]$ ansible-playbook -i infoblox.py debug.yml PLAY [all] *********************************************************************************************** TASK [list all hosts] ************************************************************************************ ok: [leaf01 -> localhost] => { "inventory_hostname": "leaf01" } ok: [leaf03 -> localhost] => { "inventory_hostname": "leaf03" } ok: [leaf02 -> localhost] => { "inventory_hostname": "leaf02" } ok: [leaf04 -> localhost] => { "inventory_hostname": "leaf04" } ok: [spine01 -> localhost] => { "inventory_hostname": "spine01" } ok: [spine02 -> localhost] => { "inventory_hostname": "spine02" } PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************** leaf01 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 leaf02 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 leaf03 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 leaf04 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 spine01 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 spine02 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
More Information
For more information on Ansible networking check out the Ansible Networking microsite. Infoblox NIOS can now utilize Ansible Playbook that are already configuring Cisco IOS, NX-OS, IOS-XR, Juniper JunOS, Arista EOS and much more.